Cannabis Tincture vs. Oil: Exploring the Key Differences 🌿
When navigating the world of cannabis products, many European consumers find themselves confused between cannabis tinctures and cannabis oils. While these products may appear similar at first glance, they possess distinct characteristics that make each suitable for different needs and preferences. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed choice about which product best suits your requirements.
Our comprehensive guide will help you understand the fundamental differences between cannabis tinctures and oils, from their extraction methods to their effects and applications. Whether you’re looking to buy cannabis products online or simply want to expand your knowledge, this guide provides everything you need to know.
What Is Cannabis Tincture? 🧪
A cannabis tincture represents one of the oldest forms of cannabis medicine, traditionally made by soaking cannabis plant material in high-proof alcohol. THC tinctures are traditionally made using alcohol, while THC oils use carrier fats. This alcohol-based extraction method draws out the active cannabinoids, creating a potent liquid that can be administered sublingually (under the tongue) for rapid absorption.
The beauty of tinctures lies in their versatility and precision. They typically come with a dropper, allowing users to measure exact doses easily. Typically administered under the tongue, tinctures generally takes effect much faster than edibles because there are blood vessels under the tongue where cannabidiol can enter the bloodstream immediately.
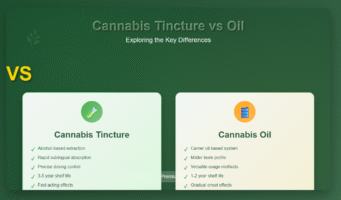
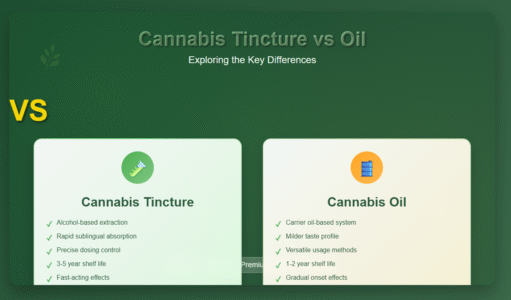
Key Characteristics of Cannabis Tinctures:
- Alcohol-based extraction process
- Sublingual administration for rapid onset
- Precise dosing capabilities
- Longer shelf life due to alcohol preservation
- Often has a stronger, more medicinal taste
How to Buy the Best Cannabis Tinctures in Europe 💡
When shopping for quality cannabis tinctures, European consumers should prioritize products from reputable sources. At Weedmarihuana.eu, we offer premium tinctures that meet strict quality standards. Look for products that provide detailed cannabinoid profiles and third-party testing results.
Important factors to consider:
- Concentration levels (measured in mg/mL)
- Full-spectrum vs broad-spectrum formulations
- Organic sourcing and extraction methods
- Proper labeling and dosage instructions
What Is Cannabis Oil? 🛢️
Cannabis oil, on the other hand, refers to extracts that use carrier oils rather than alcohol as the base. CBD oil is made by infusing cannabis in a carrier oil, while CBD tincture is traditionally created by soaking cannabis in alcohol to extract the compounds. Common carrier oils include coconut oil, hemp seed oil, and MCT oil.
Cannabis oils are created through various extraction methods, most commonly CO2 extraction or ethanol extraction, followed by mixing the concentrated extract with a carrier oil. This process results in a product that’s often more palatable than alcohol-based tinctures.
Key Characteristics of Cannabis Oils:
- Oil-based carrier system
- Milder taste compared to tinctures
- Versatile application methods
- Slower onset when taken orally
- Various carrier oil options available
Where to Order Premium Cannabis Oils Online 🛒
Finding quality cannabis oils in Europe has become easier with reputable online dispensaries. Our cannabis oil collection features various potencies and formulations suitable for different needs. Whether you’re seeking CBD-dominant oils for wellness or THC-rich options for therapeutic purposes, proper sourcing is essential.
Cannabis Tincture vs Oil: Extraction Methods Comparison ⚗️
The extraction method represents the most fundamental difference between tinctures and oils. Typically, CBD oil uses a carbon dioxide extraction method, while tinctures use alcohol to extract the substance. This difference in extraction significantly impacts the final product’s characteristics.
| Aspect | Cannabis Tinctures | Cannabis Oils |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Solvent | High-proof alcohol (ethanol) | CO2 or ethanol followed by carrier oil |
| Secondary Base | Alcohol remains in the final product | Carrier oils (coconut, MCT, hemp seed) |
| Extraction Efficiency | High cannabinoid binding | Moderate to high, depending on the method |
| Shelf Life | 3-5 years (alcohol preserves) | 1-2 years (oil can degrade) |
| Taste Profile | Strong, medicinal, alcohol burn | Milder, nutty, or neutral depending on carrier |
| Production Time | Several weeks for traditional methods | Days to weeks depending on technique |
Which Cannabis Product Has Better Bioavailability? 📊
Bioavailability refers to how much of the active compounds your body actually absorbs and utilizes. Studies have shown that the sublingual absorption of cannabinoids through tinctures can lead to an efficacy rate of up to 35% in some cases. This makes tinctures particularly attractive for users seeking quick relief.
Cannabis oils, when taken sublingually, offer similar bioavailability. However, when swallowed, oils must pass through the digestive system, reducing their bioavailability compared to sublingual administration. Edibles, capsules, and tinctures generally have a lower bioavailability, but their psychoactive effects last longer than other consumption methods.
Bioavailability Comparison:
- Sublingual tinctures: 15-35% bioavailability
- Sublingual oils: 15-30% bioavailability
- Oral oils: 6-20% bioavailability
- Oral tinctures: 6-20% bioavailability
How to Use Cannabis Tinctures vs Oils Effectively 💪
Tincture Usage:
- Shake the bottle well before use
- Use the dropper to measure desired dose
- Place drops under tongue
- Hold for 30-90 seconds before swallowing
- Effects typically begin within 15-45 minutes
Oil Usage:
- Start with a low dose (1-2 drops)
- Can be taken sublingually or mixed with food
- Sublingual: Hold under tongue for 60-90 seconds
- Oral: Swallow directly or mix with meals
- Effects vary: 15-45 minutes (sublingual), 30-120 minutes (oral)
Both products allow for precise dosing, but tinctures often provide more consistent measurements due to alcohol’s uniform consistency.
Why Buy Cannabis Concentrates and Extracts in Europe? 🌍
The European cannabis market has evolved significantly, offering consumers access to high-quality cannabis concentrates and extracts. When you order cannabis products from established suppliers, you gain access to lab-tested products that meet stringent quality standards.
Benefits of European cannabis products:
- Strict regulatory compliance
- Third-party testing for purity and potency
- Sustainable cultivation practices
- Discrete packaging and shipping
- Professional customer service
Cannabis Tincture vs Oil for Medical Applications 🏥
Medical cannabis patients often prefer one format over another based on their specific conditions and treatment goals. Full-spectrum CBD oil includes all of the compounds in the cannabis plant, including some THC, which may be more potent.
Tinctures excel for:
- Rapid relief needs
- Precise dosing requirements
- Long-term storage without refrigeration
- Sublingual medication preferences
Oils work better for:
- Sensitive palates (milder taste)
- Cooking and food integration
- Topical applications (some formulations)
- Gradual effect preferences
Best Cannabis Strains for Tinctures and Oils 🔥
Different cannabis strains work better for specific extraction methods. High-resin strains typically produce the most potent tinctures and oils. Popular strains for extraction include:
- OG Kush – Balanced effects, high potency
- Blue Dream – Smooth flavor profile, versatile
- Afghan Kush – Heavy resin production, relaxing effects
- Amnesia Haze – Uplifting effects, terpene-rich
How to Store Cannabis Tinctures and Oils Properly 📦
Proper storage ensures your cannabis products maintain their potency and safety over time. Both tinctures and oils require specific storage conditions to prevent degradation.
Tincture Storage:
- Store in cool, dark places
- Keep bottles tightly sealed
- Avoid temperature fluctuations
- Can last 3-5 years when stored properly
Oil Storage:
- Refrigeration recommended for longer shelf life
- Protect from light and heat
- Use within 1-2 years for optimal potency
- Check for rancidity or off odors
Cannabis Tincture vs Oil: Cost Analysis 💰
Cost considerations play a significant role in choosing between tinctures and oils. Generally, tinctures command higher prices due to their longer production time and alcohol costs. However, they also offer longer shelf life, potentially providing better long-term value.
Pricing factors:
- Production complexity affects base costs
- Potency levels determine price per dose
- Brand reputation influences premium pricing
- Volume purchases often reduce per-unit costs
When you buy cannabis online, consider the cost per milligram of active cannabinoids rather than just the bottle price.
Which Is Better for Beginners: Tinctures or Oils? 🌱
New cannabis users often find oils more approachable due to their milder taste and familiar oil-based format. However, tinctures offer more precise dosing control, which can be crucial for finding the right therapeutic dose.
Beginner-friendly features:
- Oils: Milder taste, versatile usage, familiar format
- Tinctures: Precise dosing, faster effects, longer shelf life
We recommend starting with either format at the lowest possible dose and gradually increasing until desired effects are achieved.
Key Takeaways 📝
Understanding the differences between cannabis tinctures and cannabis oils empowers you to make informed decisions about your cannabis consumption. While both products offer unique advantages, your choice should depend on your specific needs, preferences, and intended usage.
Remember these essential points:
- Tinctures use alcohol extraction and offer rapid sublingual absorption
- Oils use carrier oils and provide versatile consumption options
- Both allow for precise dosing when used correctly
- Storage requirements differ between the two formats
- Quality sourcing remains crucial regardless of your choice
Frequently Asked Questions 🤔
What’s the main difference between cannabis tincture and oil?
The primary difference lies in the extraction method and base solution. CBD tincture uses alcohol as a base and solvent to extract and suspend the CBD, and CBD oil is created by using CO2 or ethanol extraction methods before suspending the CBD in a carrier oil. This affects taste, bioavailability, and shelf life.
Which is more potent: tinctures or oils?
A: Potency depends on the concentration of cannabinoids rather than the format itself. CBD oils usually have higher concentrations of CBD compared to tinctures, but individual products vary significantly. Always check the mg/mL concentration on product labels.
Can I make cannabis tinctures and oils at home?
Yes, both can be made at home, but safety precautions are essential. CBD tinctures can even be made at home through methods like steeping CBD-rich hemp flowers in high-proof grain alcohol, then cooking the mixture over low heat for several hours. However, professional products offer consistency and safety testing.
How long do the effects last for tinctures vs oils?
When taken sublingually, both tinctures and oils have similar onset times (15-45 minutes) and duration (2-6 hours). Sublingual use has higher bioavailability than edibles but lower than inhalation. Oral consumption extends both onset time and duration for either format.
Are there any side effects specific to tinctures or oils?
Side effects are generally related to cannabinoid content rather than the delivery method. However, some people may be sensitive to alcohol in tinctures or specific carrier oils. Some prefer cannabis oil tinctures because they don’t like the taste of alcohol or they are sensitive to alcohol.
Which format is better for cooking and recipes?
Oils integrate more seamlessly into recipes due to their fat-based composition. Alcohol-based tinctures can affect flavor more significantly and may require cooking modifications to account for alcohol content. However, both can be used in culinary applications.
Where can I buy high-quality cannabis tinctures and oils in Europe?
Quality cannabis products are available through licensed dispensaries and reputable online retailers. When shopping, prioritize vendors that provide lab testing results, detailed product information, and comply with local regulations. Visit our shop for premium cannabis products with European shipping.




 Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español